常州江苏大学工程技术研究院
Changzhou Engineering and Technology Institute of Jiangsu University
Welcome to Changzhou Engineering and Technology Institute of Jiangsu University!
Technical field
The invention belongs to the metal materials metallurgy and heat treatment technical field, and relates to an interfacial regulating heat treatment method of high entropy alloy particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites, in particular a heat treatment method of regulating (FeCoNiCrAlCu)p/2024A1 composites interfacial.
Technical background
High entropy alloy is a new alloy system with unique microstructure, high hardness and strength, and good thermal stability at high temperature. Due to the natural interfacial bonding property between metal and metal, the interfacial wettability and interfacial compatibility between high entropy alloy and aluminum alloy matrix are goo. If the alloy with high entropy is used as the composite phase to strengthen the aluminum alloy, and the interface characteristics is also adjusted, the strength and plasticity of the composite material can be improved, which has a wide application prospect in automotive, aerospace and other fields.
Microwave heating is to absorb microwave by the material inside the metal, and convert it into heat energy. At the same time, the external high dielectric loss SiC crucible heats the material through thermal radiation, so the whole material almost heats up at the same time, the temperature gradient is smaller than other heating methods, and the heating speed is faster, so that the grain is not too big during heat treatment. At the same time, thanks to the electromagnetic force generated by microwave heating, the distribution of the enhanced phase can be more dispersed.
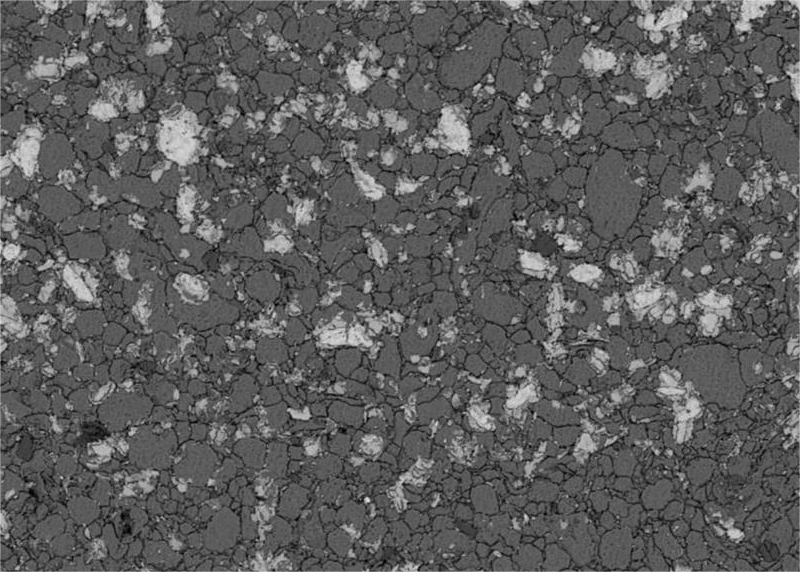
The solute concentration difference between the reinforced particles and the matrix of high-entropy alloy reinforced aluminum matrix composites is large, which can promote the mutual diffusion of elements between them. Al is the largest content, and its activity is the highest in solution treatment, which is more conducive to diffusion. The mixing enthalpy of Al and Ni is -22KJ/mol, and the two are easy to combine, while Cu is easy to form segregation. Therefore, at the interface of the composite material, a micron diffusion layer composed of Al, Ni, Cu and other elements is formed.
The load between the reinforcement and the matrix is transferred through the interface. However, at present, the measures adopted by researchers to improve strength and toughness are to optimize the types and properties of strengthening particles, and the control of interface characteristics is relatively lack, which can not make the bonding strength and thickness of the composite interface reach the ideal state, often resulting in the high entropy alloy to strengthen the strength and toughness of aluminum matrix composites not being fully developed.
In view of this, in order to regulate the interface characteristics of high entropy alloy particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material, so as to further improve the strength and toughness of the composite material, the present invention proposes a heat treatment method for regulating (FeCoNiCrAlCu)p/2024A1 composite material interface based on the internal relationship between heat treatment system, particle/matrix interface characteristics and mechanical properties.
Compared with the prior technology, the beneficial effects of the invention are as follows:
The invention relates to a composite material with an interface layer of certain thickness between the high entropy alloy particle and the matrix. The invention combines two different heat treatment processes of "solid solution" and "aging", uses nano-indentation technology to detect, and promotes the diffusion of the interface of the composite material, which makes the thickness of the interface bonding layer more ideal, and improves the interface bonding strength. At the same time, the aging treatment eliminates the residual stress, reduces the probability of cracking of the material, and realizes the strengthening and toughening of the material.
Among the composite materials mentioned in the invention, the high-entropy alloy of strengthening phase and the aluminum matrix have great differences in thermal expansion and other properties. Compared with slow cooling, the residual stress of the room temperature water bath quenching after the first heat treatment is larger. Twin crystals appear in the near interface area of the composite material, and the critical shear stress of the twin crystals is larger, which can hinder the deformation of the crystal so as to strengthen the material.
The invention makes full use of the characteristics of microwave heating "low temperature fast burning, selective heating", more effectively promoting the diffusion of interfacial layer elements, and regulating the thickness and bonding strength of interfacial layer, so that the grain will not overgrow during heat treatment. Thanks to the effect of microwave, the microstructure of the material is denser and the strengthening phase is more dispersed. At the same time, microwave heating energy consumption is low, the equipment is simple, and easy to operate and popularize.
Address: Fifth Floor, Block C of Tianrun Technology Building, No. 801 Changwuzhonglu, Wujin District, Changzhou, Jiangsu Province, China
Cell: 13813651639(Mrs Shi)
Email: 1320084251@qq.com
Web: www.czujs.cn