常州江苏大学工程技术研究院
Changzhou Engineering and Technology Institute of Jiangsu University
Welcome to Changzhou Engineering and Technology Institute of Jiangsu University!
Research background and significance
China's existing high energy consumption residential area is more than 40 billion square meters, and the average cooling energy consumption of these buildings is three times that of the corresponding buildings in developed countries. More than 30% of building energy consumption is used in building cooling. Research to reduce building cooling energy consumption has become an inevitable trend in the development of green building energy conservation, and is with great scientific, economic and social value.
At present, the main ways to achieve building cooling include: 1, the use of HVAC equipment; 2, the use of natural low-temperature objects. 3, the use of rock wool, slag wool and other thermal insulation materials with low thermal conductivity as wall insulation layer. There are difficulties such as high energy consumption and bad performance in environmental protection.
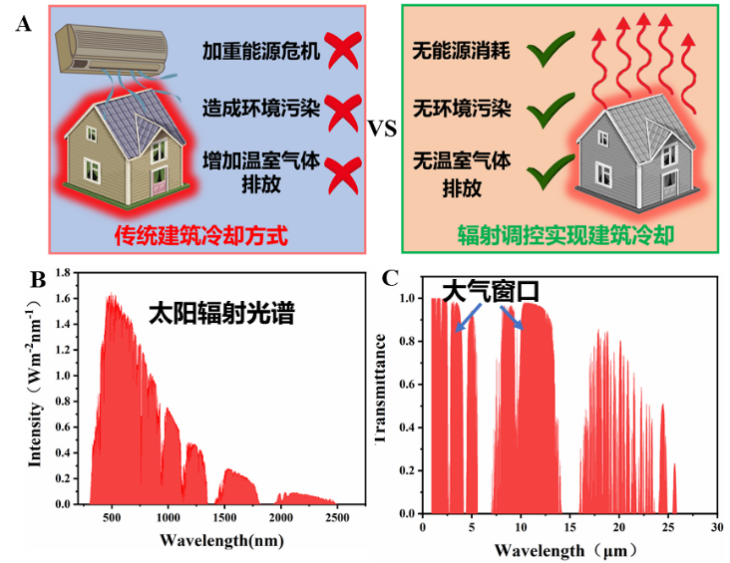
Compared with traditional methods to enhance building heat transfer and convection, radiation-controlled cooling has the advantages of no energy consumption, no environmental pollution, no operating media and convenient operation (see Figure 1A). Solar radiation band: The total power density of solar radiation (0.3~4μm) can reach 1000 Wm−2 (Figure 1B). Reducing solar radiation absorption and enhancing solar radiation reflection have positive effects on reducing heat input in summer. Infrared radiation band: regulate the infrared radiation characteristics of the building (4~20μm), especially in the atmospheric window band (3~5μm and 8~13μm) to enhance the heat dissipation of the building (see Figure 1C). Due to the non-coincidence of the solar radiation band (0.3~3μm) and the building infrared radiation band (4~20μm), the two radiation bands need to be selectively regulated: it can reflected or scattered solar radiation to the maximum, and maximize the radiation performance of the building's atmospheric window band.
Technology maturity
Laboratory performance tests have been completed.
Technological advancement
This work is in line with the national strategy of energy conservation, emission reduction and green development, aiming at the current research gap in the lack of efficient solutions in terms of high energy consumption and pollution of buildings.
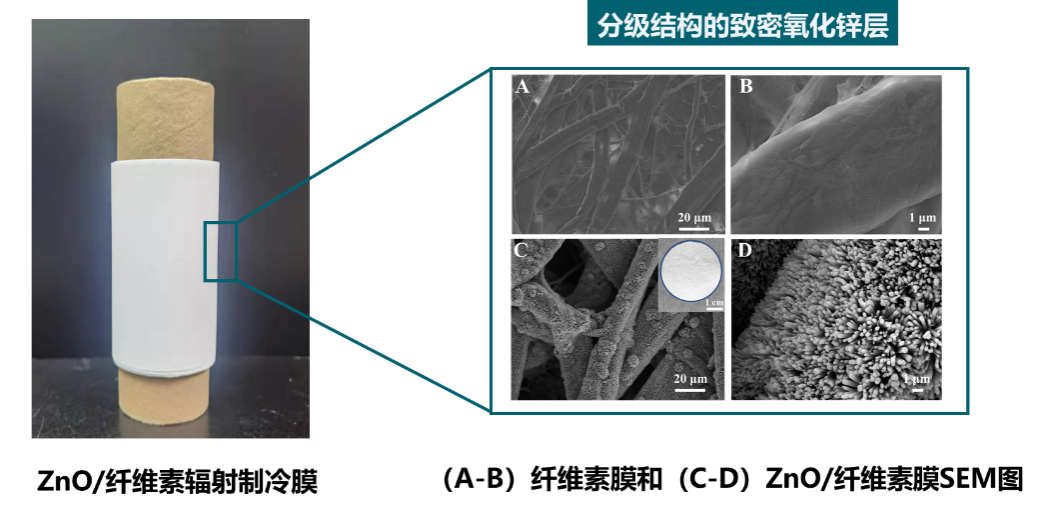
Cellulose is selected as the main functional body, which has the advantages of wide source and simple cost.
Expand the building cooling strategy from a high-energy compressor or heat pump to a no-energy all-weather (day and night) multi-band radiation control, which can achieve a cooling of 6℃ on the building wall.

Expected benefit
Jointly realize the expanded production of radiation refrigeration film.
The type of business you want to work with
Solar energy utilization, new building materials and other related enterprises.
Address: Fifth Floor, Block C of Tianrun Technology Building, No. 801 Changwuzhonglu, Wujin District, Changzhou, Jiangsu Province, China
Cell: 13813651639(Mrs Shi)
Email: 1320084251@qq.com
Web: www.czujs.cn