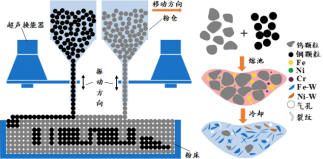
Interface construction and performance strengthening technology for additive manufacturing of heterogeneous materials
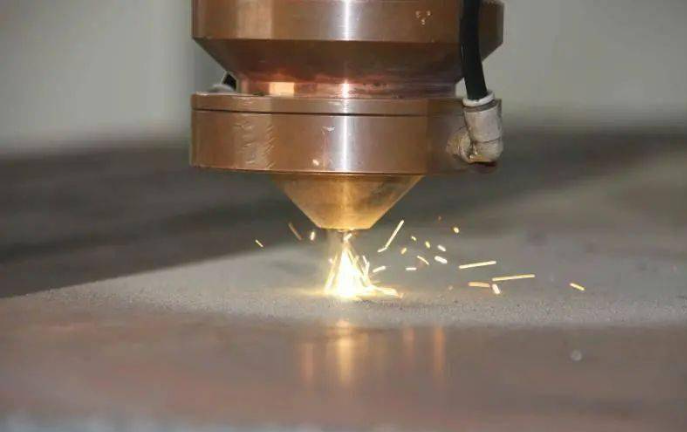
1. The technological advancement of the results Common bonding methods of heterogeneous materials include welding, powder metallurgy, solid sintering and other processing processes. These traditional manufacturing techniques have limitations in forming heterogeneous materials and it is difficult to prepare structures with complex three-dimensional shapes to meet different application requirements. Additive manufacturing has great advantages in the preparation of heterogeneous material parts. It can achieve the desired performance and structure in different parts with complex shapes by changing the transportation or laying ratio of different materials in real time. The figure shows the additive manufacturing process diagram of heterogeneous materials based on ultrasonic vibration feeding powder. However, there are many defects such as pores, cracks and poor fusion at the interface of additive manufacturing of heterogeneous materials, which become the technical bottleneck restricting its development and hindering its industrial application. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the interface defects in additive manufacturing of heterogeneous materials to realize the controlled preparation and property control of components. By constructing the heterogeneous interface structure, the temperature and solute distribution in the heterogeneous interface molten pool can be controlled in a directional way, thus reducing the fluidity difference caused by the difference of material properties such as melting boiling point, density and viscosity. By constructing a numerical model of multi-physical field coupling, the development law of heterogeneous material molten pool under multiple laser reflection can be revealed, the evolution process of keyhole molten pool at the heterogeneous interface can be verified, and the forming mechanism of heterogeneous material interface can be clarified. At the same time, by deeply exploring the growth and distribution law of intermetallic compounds at the interface, we can precisely control the microstructure evolution and restrain the defects, and solve the core scientific problem behind the technical bottleneck. 2. Maturity of technology This technique has been applied to the connection of tungsten/steel heterogeneous material members. Tungsten/steel heteromaterial components have become the preferred composite structure for diverters in future nuclear fusion reactors due to their excellent anti-ionization radiation properties. At the same time, tungsten/steel heteromaterial components have also been applied in armor-piercing shells, rocket thruster nozzles, penetration weapons, die casting molds, aerospace and many other fields. By constructing heterogeneous interfacial structures, this technique can optimize the non-uniform heat/mass distribution, deformation, delamination and crack caused by thermal stress and brittle intermetallic compounds (such as Fe-W), eliminate forming defects and improve the formability of heterogeneous structures. The figure shows a shaped sample of a tungsten/steel heterocomponent. In addition, the technology has realized the processing of copper/steel, titanium/steel, tungsten/copper, steel/ceramic and other dissimilar material components, and has realized the integrated forming of complex structures. The picture shows the copper/steel goldfish pendant and steel/ceramic double helix structure.3. The intellectual property Relying on Jiangsu University, this technical achievement has been approved by National Natural Science Foundation and Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation.We have also published five SCI papers. 4. Expected benefits and types of enterprises to cooperate with This technology is expected to realize the joint forming of dissimilar materials in complex structures, including the direct forming of metal-metal, nonmetal-nonmetallic and metal-nonmetallic material combinations. The requirements of enterprises that want to cooperate include different physical and chemical properties in different parts of a single component, such as local high temperature resistance, high thermal conductivity, chemical corrosion resistance, high wear resistance, and complex shape of the component. The types of enterprises include medical, die casting mold, aerospace, automotive and parts, agricultural machinery and engineering machinery and new material fields.
View more